진스
5. Class 객체지향언어 본문
728x90
class

- class는 object(인스턴스)를 만들 수 있는 틀이다
- class 자체에는 data가 들어있지 않음
- 틀(template)을 정의해서 한 번만 선언 한다
- class는 정의만 한 것이라서 실재 메모리에 올라가지 않음
object

- class를 이용해서 data를 넣어서 만드는 것이 object다
- class를 이용해서 새로운 instance를 생성하면 그게 바로 object가 되는 것
- object는 class를 이용해서 무수히 많이 만들 수 있다
- class를 이용해 만든 object는 실재 메모리에 올라간다
- ES6에 도입
- prototype-based 기반으로 그 위에 문법만 class가 추가됨 (문법적 설탕)
- Object-oriented programming (객체 지향 프로그래밍)
- class: template
- object: instance of a class (class의 인스턴스)
1. Class 선언과 Object 생성
class Person {
// constructor
constructor(name, age) {
// fields
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// methods
speak() {
console.log(`${this.name}: hello!`);
}
}
const ellie = new Person(`ellie`, 20); // 인스턴스(object) 생성
console.log(ellie, typeof ellie); // > Person {name: "ellie", age: 20} "object"
console.log(ellie.name); // > ellie
console.log(ellie.age); // > 20
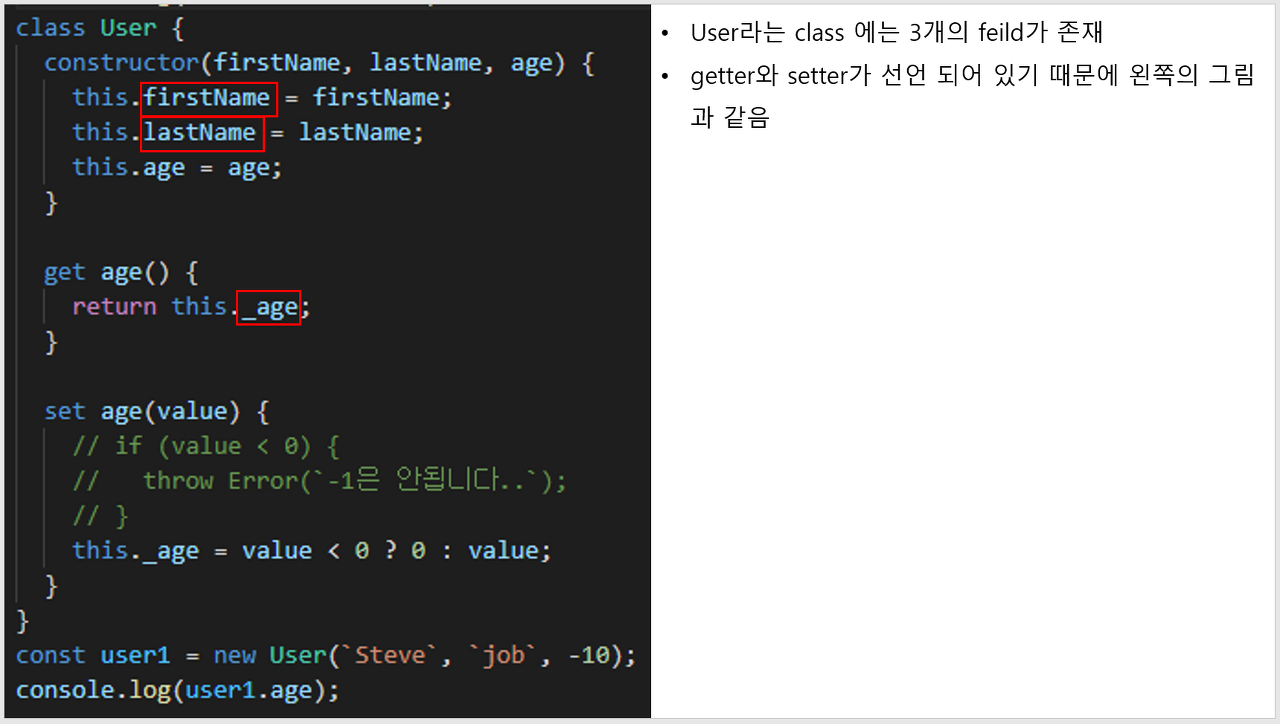
ellie.speak(); // > ellie: hello!2. Getter & Setter
class User {
// 생성자 필드
constructor(firstName, lastName, age) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.age = age;
}
// getter
get age() {
return this._age;
}
// setter
set age(value) {
// if (value < 0) {
// throw Error(`-1은 안됩니다..`);
// }
this._age = value < 0 ? 0 : value; // 생성자 필드명 앞에 _ 를 붙이는게 관습
}
}
const user1 = new User(`Steve`, `job`, -10); // set
console.log(user1.age); // get사용자가 class를 잘못 사용해도 방어적인 자세로 만들수 있도록 해주는 것이 getter와 setter 이다.


3. Fields (public, private)
- 최근에 나와서 아직 쓰기에는 무리가 있음.. 쓰려면 babel 로..
class Experiment {
publicField = 2; // 그냥 정의하면 public
#privaterField = 0; // #(해쉬) 기호를 붙이면 private
}
const experiment = new Experiment();
console.log(experiment.publicField); // > 2 : 접근 가능
console.log(experiment.privaterField); // > undefined : 접근 불가능4. Static properties, methods
- static은 object마다 할당되는게 아니라 class 자체에 붙어있음
- static 필드/메소드를 호출 할 때는 class 이름을 이용해서 호출 해야
- object에(들어오는 data에) 상관 없이 공통적으로 class에서 쓸 때, 그러면 메모리에 사용을 조금 더 줄여줌
class Article {
static publisher = `Dream Coding`; // static 필드 정의
static printPublisher() { // static 메소드 정의
console.log(`print: ${Article.publisher}!!`);
}
}
const article1 = new Article();
console.log(article1.publisher); // > undefined
console.log(Article.publisher); // > Dream Coding
Article.printPublisher(); // > print: Dream Coding!!5-1. Inheritance (상속)
- 부모 class에 있는 모든 것들이 자식 class에 포함이 됨
- 공통되어지는 값들을 extends 키워드로 재사용 할 수 있다
- 부모 class의 값을 변경하면 자식(상속 받은) class의 값들도 자동으로 변경됨
5-2. Polymorphism (다형성)
- 필요한 메서드를 재정의 해서 사용할 수 있다 (오버라이딩)
- 오버라이딩 한 상태에서 부모 class의 메서드를 사용하고 싶으면 super 키워드를 사용하면 된다
// 부모 class
class Shape {
constructor(width, height, color) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.color = color;
}
draw() {
console.log(`drawing ${this.color} color of`);
}
getArea() {
return this.width * this.height;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {}
class Triangle extends Shape {
draw() {
super.draw(); // 오버라이딩 해도 부모 class 메소드 호출 쌉가능
console.log(`📐`);
}
// 오버라이딩(다형성)
getArea() {
return (this.width * this.height) / 2;
}
}
const rectangle = new Rectangle(20, 20, `blue`);
rectangle.draw();
console.log(rectangle.getArea());
const triangle = new Triangle(20, 20, `red`);
triangle.draw();
console.log(triangle.getArea());6. Class checking: instanceOf
- instanceOf 키워드 왼쪽에 object가 오른쪽에 class의 인스턴스인지 아닌지 체크
- JS에서 만든 모든 object class들은 Object를 상속 받아져 있음, 그 말은 즉, 어떤 object든지 Object에 존재하는 공통적인 메소드들을 쓸 수 있음
console.log(rectangle instanceof Rectangle); // > true
console.log(triangle instanceof Rectangle); // > false
console.log(triangle instanceof Triangle); // > true
console.log(triangle instanceof Shape); // > true
console.log(triangle instanceof Object); // > trueJavaScript referencedeveloper.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference
JavaScript reference - JavaScript | MDN
This part of the JavaScript section on MDN serves as a repository of facts about the JavaScript language. Read more about this reference.
developer.mozilla.org
JS object 들..
728x90
'JavaScript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 7. Array(1) (0) | 2021.04.09 |
|---|---|
| 6. Object (객체) (0) | 2021.04.09 |
| 4. Function (0) | 2021.04.09 |
| 3. 연산 / 반복문 (0) | 2021.04.09 |
| 2. 데이터 타입 (0) | 2021.04.09 |
Comments


